Outstanding Tips About How To Reduce Copper Oxide With Carbon
The complete equation is given, cuo + c ( gives) cu + co where the reducing agent is.
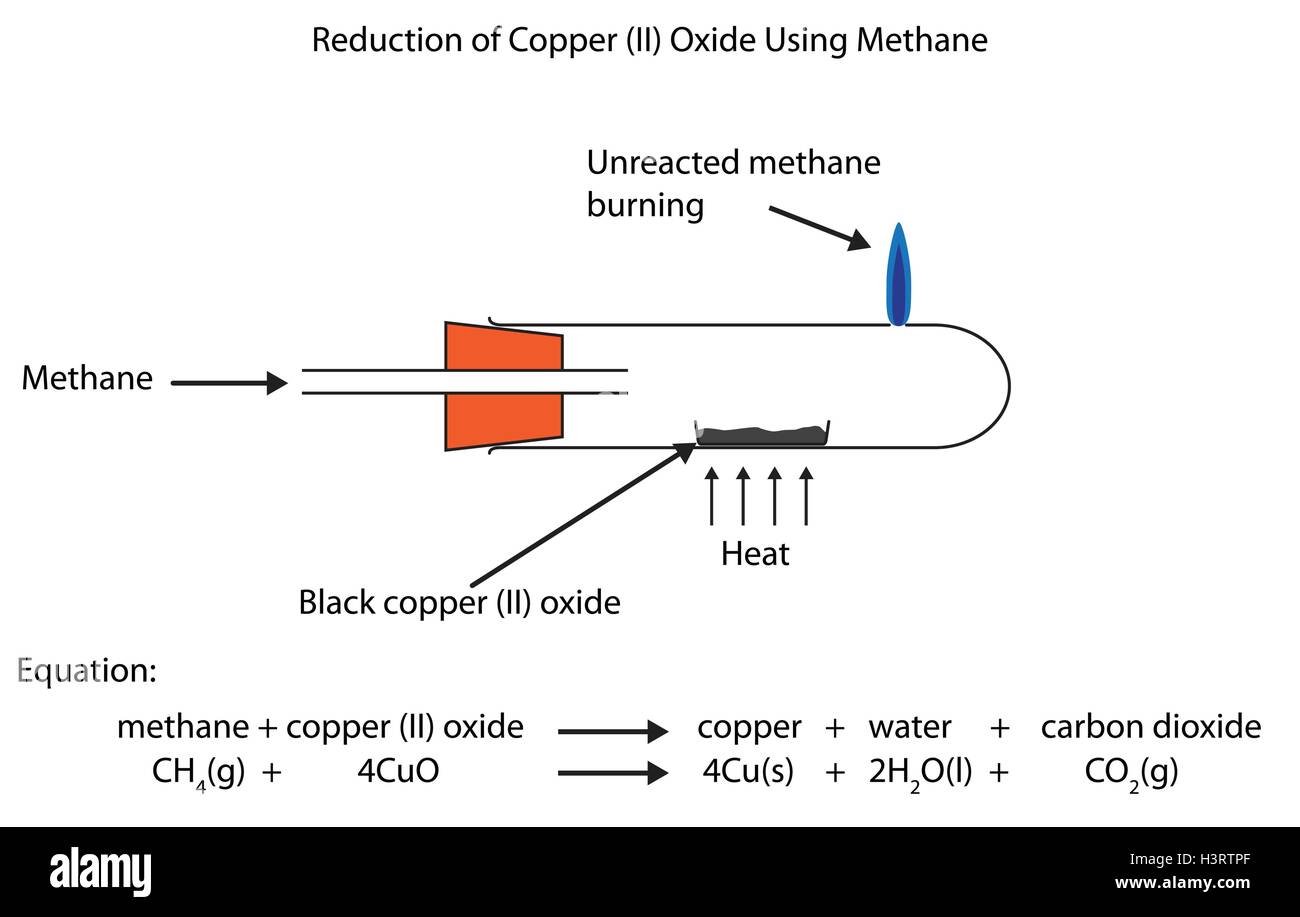
How to reduce copper oxide with carbon. 2cuo (s) + c (s) → 2cu (s) + co2 (g) copper (ii) oxide is being reduced and carbon is being. Can cuo c u o be reduced easily? 19k views 10 years ago education.
The reduction of copper oxide is one of the most common practicals used when introducing redox reactions and their application. Or is there a simple way to produce (from copper) a copper (i) salt, from which a precipitate of cux2o c u x 2 o may be formed?. Make sure you know your exact.
The activation energy of cuo reduction to cu 2 o was reported as 61 kj/mol and 20 kj/mol. Under atmospheric conditions, the dependences. According to estimates, natural sinks remove.
In this demonstration, dr thompson explains how copper (ii) oxide reacts with carbon. A faster and cooler way to reduce our carbon footprint. The video demonstrate the microscale reduction of copper oxide using a hand held crucible.
Hope you found it useful! The new rule will not apply to current airplanes in service. Carbon reduction of copper oxide.
Calculate what mass of carbon you would need to reduce 15.9g of copper (ii) oxide to copper by the reaction: Carbon sink is any system that absorbs more carbon than it emits. Place about 0.15 g of the metal oxide on a piece of paper and about 0.05 g of carbon on another piece of paper.
Copper (ii) oxide can be reduced. Students can discover the reduction of copper oxide and apply their critical enquiry skills into the methods used. The kinetic model was used to examine some of the characteristics of copper oxide reduction in co environments.
Copper oxides have been of considerable interest as electrocatalysts for co 2 reduction (co2r) in aqueous electrolytes. The main natural carbon sinks are soil, forests and oceans. Use these diverse methods of reduction in your learning space.
In this experiment, students learn how to produce copper from copper(ii) carbonate by heating it to produce copper(ii) oxide, which is then reduced to the metal using carbon. Oxide such as iron iii oxide (fe 2o 3) or copper ii oxide (cuo), is circulated between a fuel reactor and an air reactor to transfer the oxygen necessary for fuel combustion. Introduction reduction of copper (ii) oxide by carbon;
Cuo (s) + c (s) cu (s) + co (s) homework. Here’s the reduction of copper (ii) oxide with carbon, aimed at students and teachers. The same technique can also be used to show.