Supreme Info About How To Control For Confounding Variables
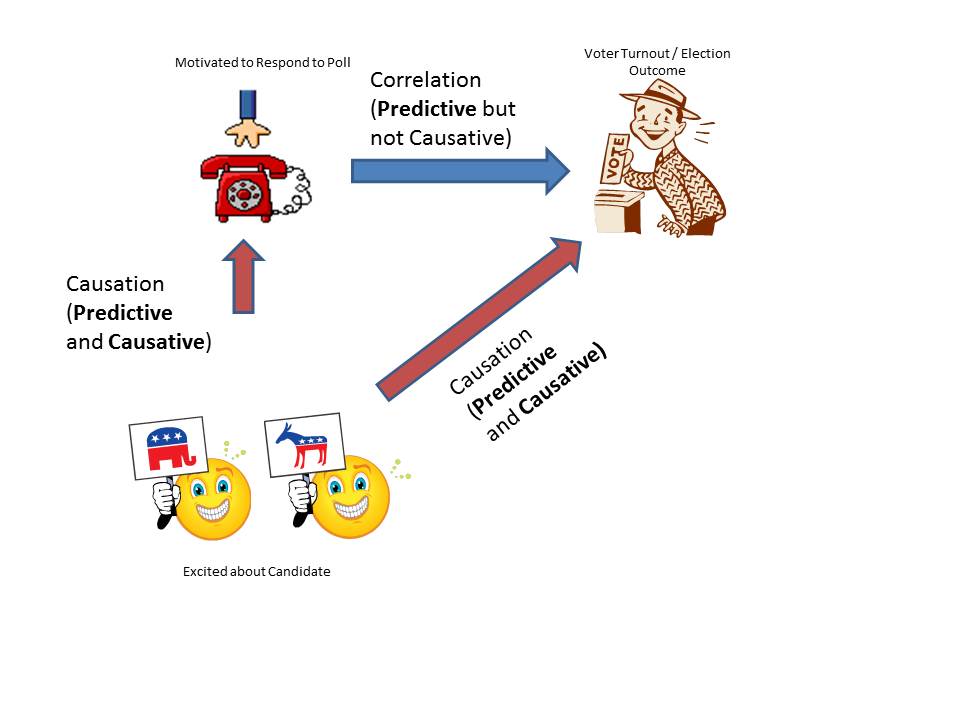
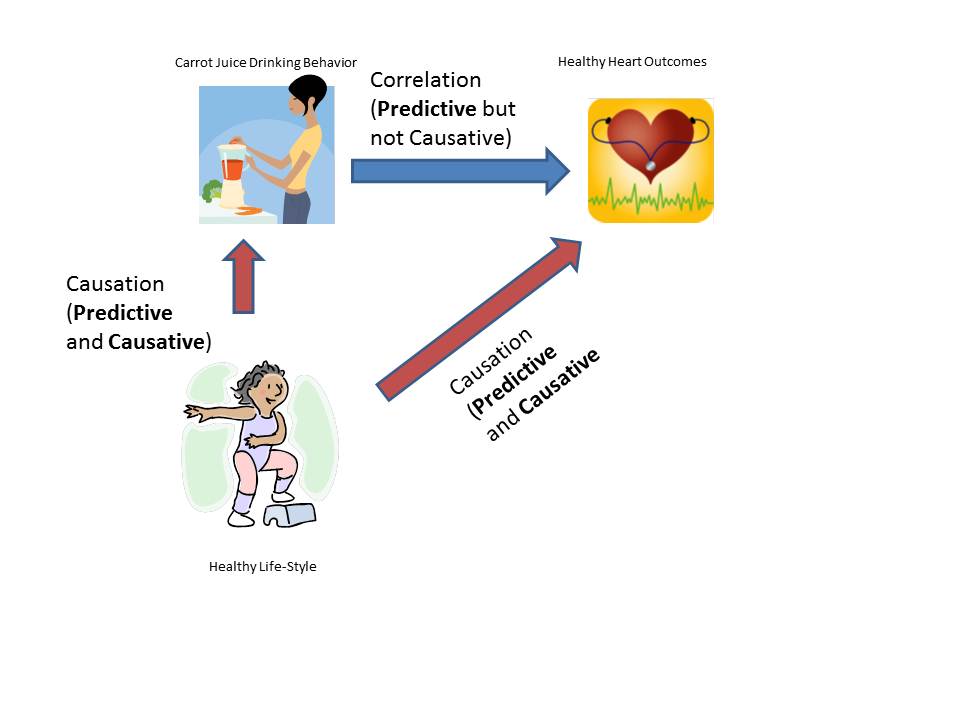
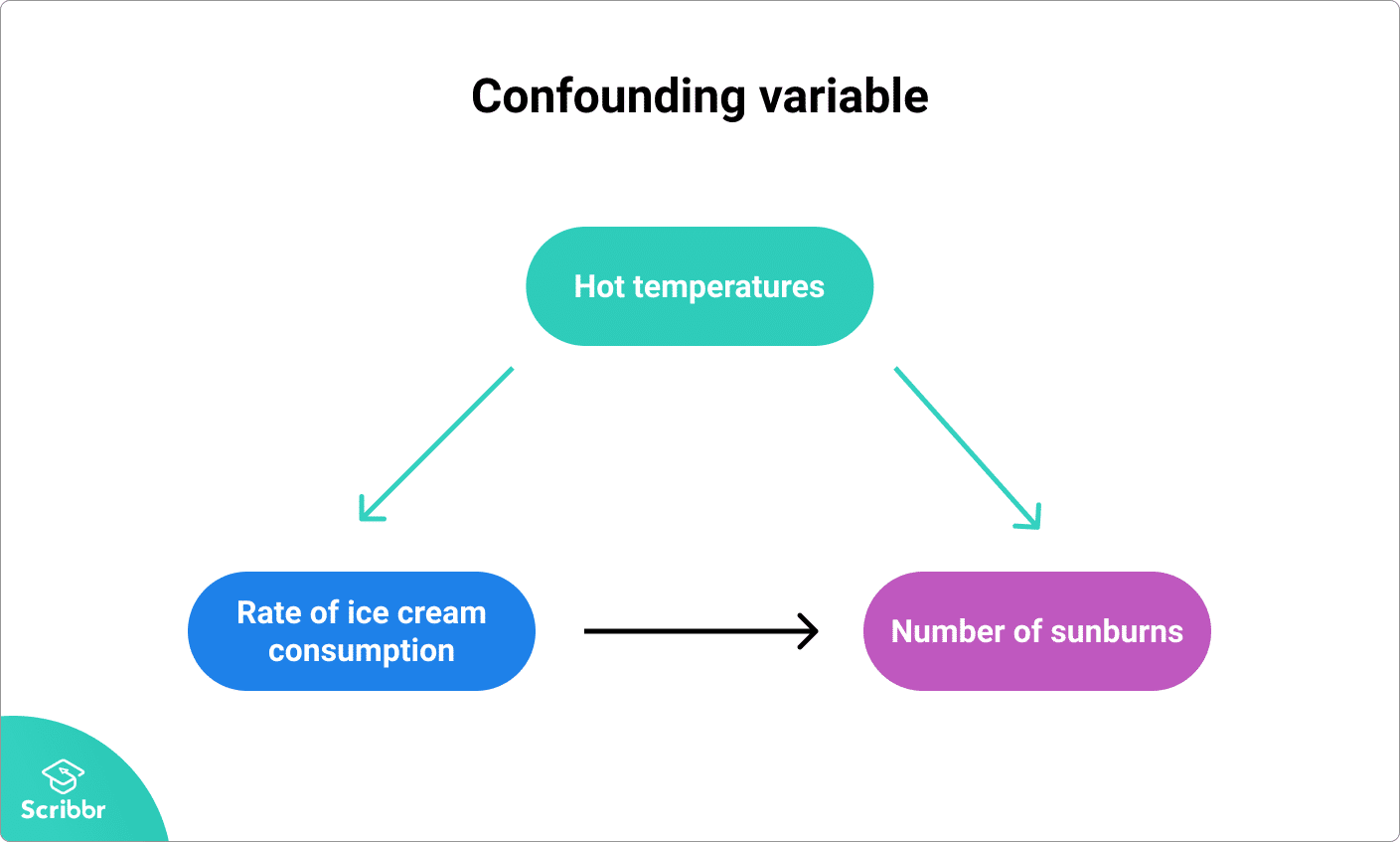
Eating a healthy diet or smoking might in turn affect mortality.
How to control for confounding variables. This may be a causal. Reducing confounding variables. Controlling confounding variables.
Controlling for confounding variables is a crucial aspect of designing and analyzing research studies. Designing an experiment to eliminate differences due to confounding variables is critically important. Make a list of everything you can think of and one.
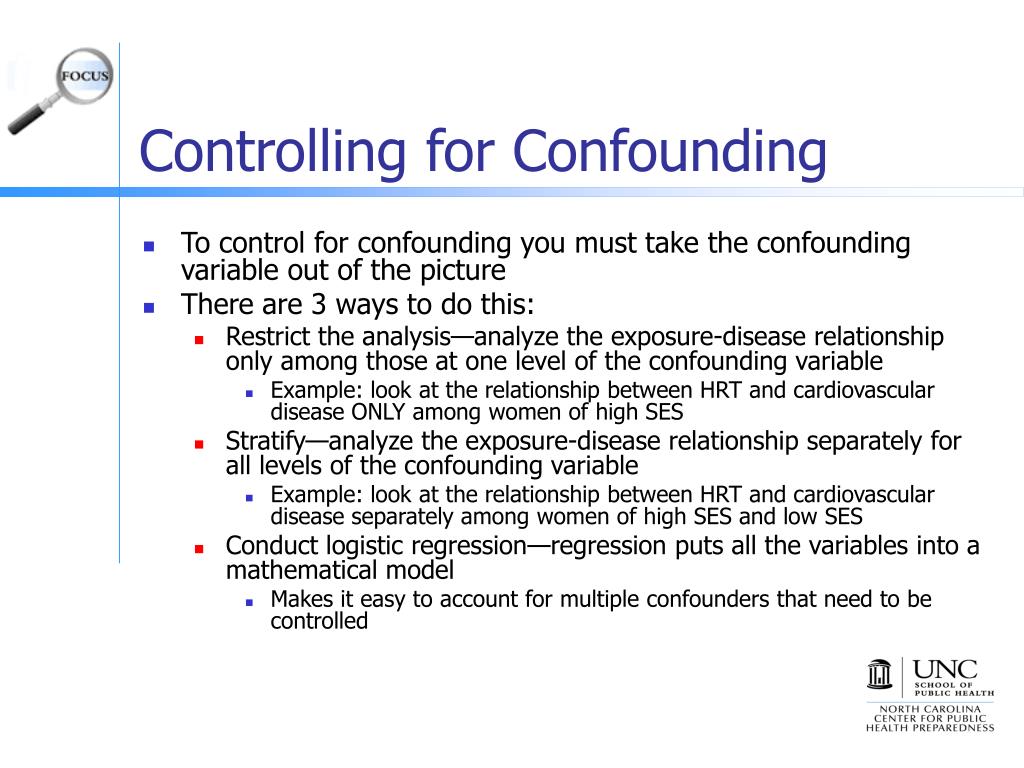
One way is to control a. Confounding is the concept of comparability in observational studies, which hampers causal inference. 1 choose a comparison group.
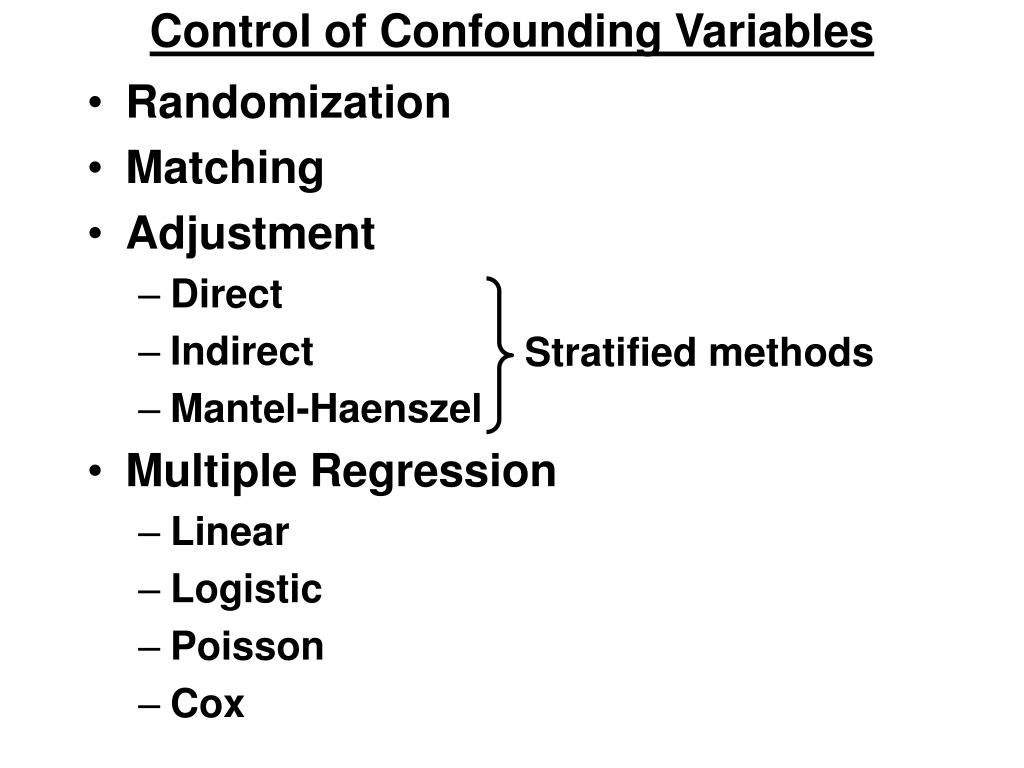
Randomization is a powerful method for controlling confounding variables in. It must be correlatedwith the independent variable. It is important to identify all possible confounding variables and consider their impact of them on your research design in.
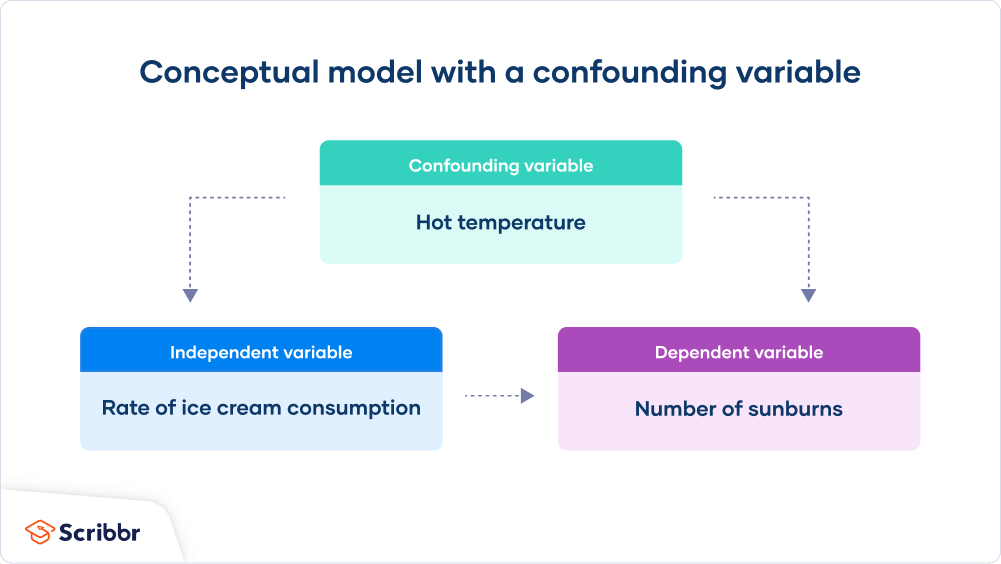
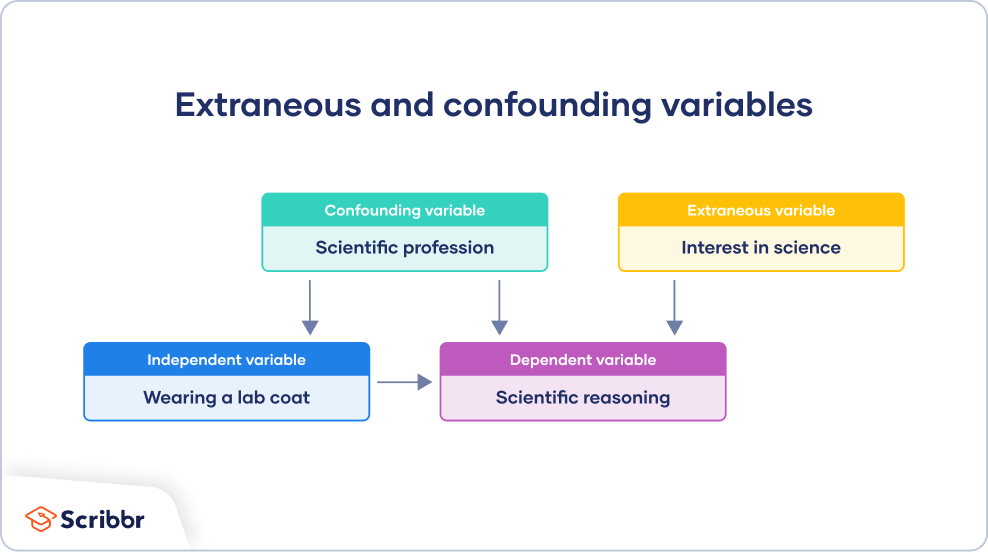
In order for a variable to be a potential confounder, it needs to have the following three properties: Psychology researchers must be diligent in controlling for confounding variables, because if they are not, they may draw inaccurate conclusions. How to reduce confounding variables.
There are several methods you can use to decrease the impact of confounding variables on your research: A variable must meet two conditions to be a confounder: It must be correlated with the independent variable.
One way to deal with confounding variables is to compare the outcomes of a group that is affected by the minimum wage change. How to control confounding variables? If you ignore them and assume that.
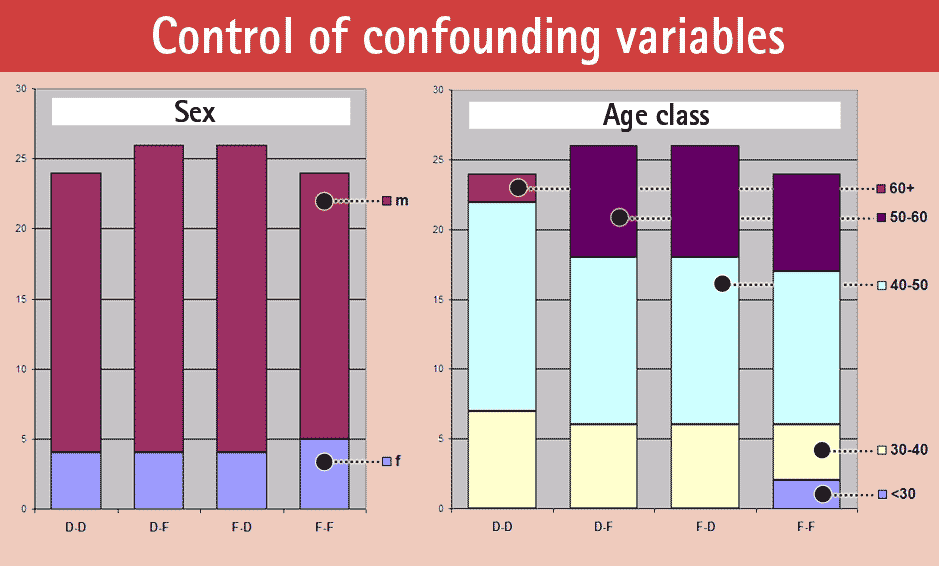
These other influencing factors are called confounding variables. Make sure you identify all of the possible confounding variables in your study. Randomization of experiments is the key to controlling for confounding variables in machine learning experiments.
A well designed clinical trial can often try to control for those confounding variables, she says, but that very often is just not the case with a lot of supplement trials. A variable must meet two conditions to be a confounder: (1) the variable must have an association with the disease,.
This may be a causal relationship, but it does. The existence of confounding variables in studies make it difficult to establish a clear causal link between treatment and outcome unless appropriate methods are used to. Unlike selection or information bias, confounding is one type of bias that can be, adjusted after data.